Clinical study overview
COMET was a 12-month, Phase 3, multicenter, long-term, open-label safety study assessing AUVELITY (twice daily) in 876 patients (rollover from prior AUVELITY studies and newly enrolled) with MDD. Efficacy measures were secondary endpoints based on newly enrolled patients (n=609).1-4 See full study design.
Long-term safety of AUVELITY from a study lasting up to 12 months1,3*
Long-term safety in the open-label COMET study was consistent with controlled clinical studies.3,5,6
Common adverse events
(≥5% of AUVELITY-treated patients)3
| Adverse event | AUVELITY (N=876) |
|---|---|
| Dizziness | 12.7% |
| Nausea | 11.9% |
| Headache | 8.8% |
| Dry mouth | 7.1% |
| Decreased appetite | 6.1% |
*The overall safety population includes all patients who received study medication.3,7
rate
8.4% (74/876) of patients on AUVELITY discontinued study participation due to adverse events.3
The most common adverse events resulting in discontinuation were dizziness (1.5%), nausea (1.1%), headache (1.0%), anxiety (0.8%), and decreased appetite (0.6%).3
Long-term safety and effectiveness were measured for
AUVELITY in an open-label study1
AUVELITY had a demonstrated safety profile in a study lasting up to 12 months. The most common adverse events experienced in ≥5% of AUVELITY-treated patients were dizziness (12.7%), nausea (11.9%), headache (8.8%), dry mouth (7.1%), and decreased appetite (6.1%). Long-term safety data up to 12 months were consistent with the controlled clinical studies.3,5,6
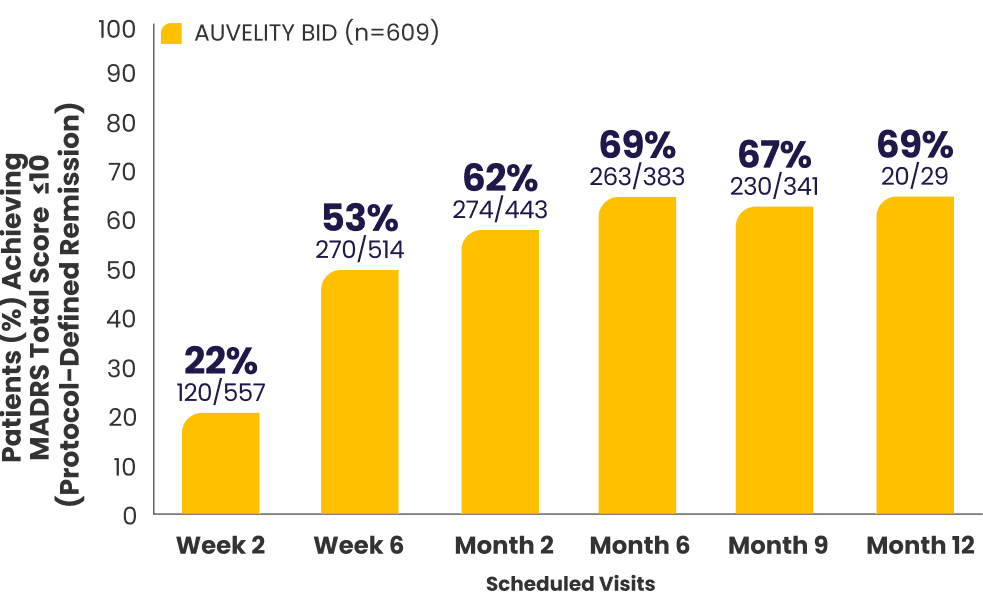
Protocol-defined remission2,4*†
MADRS total score ≤10
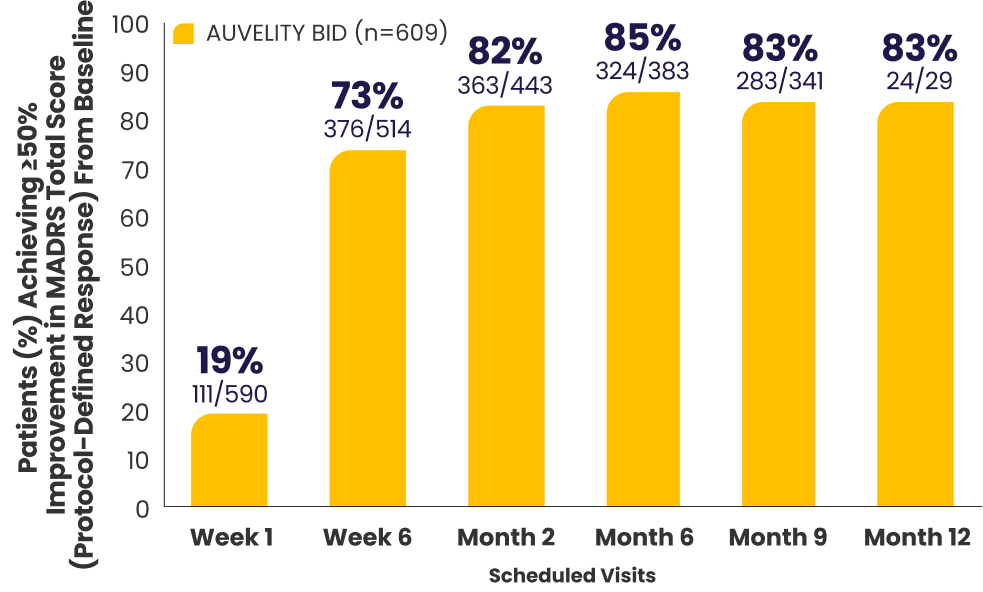
Protocol-defined response2,4*†
≥50% improvement in MADRS
total score from baseline
Data from open-label studies have limitations. As the study was not blinded or placebo-controlled, results should be interpreted with these factors in mind. Endpoints were analyzed descriptively, and statistical significance cannot be attributed.
All newly enrolled patients were assessed for efficacy through Week 6. Only patients whose MADRS scores improved by ≥25% were eligible to continue in the study. 6% of subjects met discontinuation criteria at Week 6.1,7
The decrease in patient number over time is primarily due to staggered entry into the study and the closing of the study once enrollment goals were met.1
*AUVELITY-naïve ITT population.2
†Missing data were not imputed. Efficacy data from early termination visits were included in the summary of the next scheduled efficacy assessment visit.1
BID=twice a day; ITT=intention-to-treat; MADRS=Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale.
COMET Phase 3 Study
COMET was a Phase 3, multicenter, open-label US study. Patients with MDD were treated with AUVELITY twice daily in a 12-month study. The study enrolled both patients completing a prior AUVELITY study and newly enrolled patients. The trial was concluded once at least 300 patients had been treated for 6 months and at least 100 patients had been treated for 12 months, as prespecified. At the time of study conclusion, 597 patients had reached at least 6 months, and 110 patients had reached at least 12 months of treatment.1,4,8
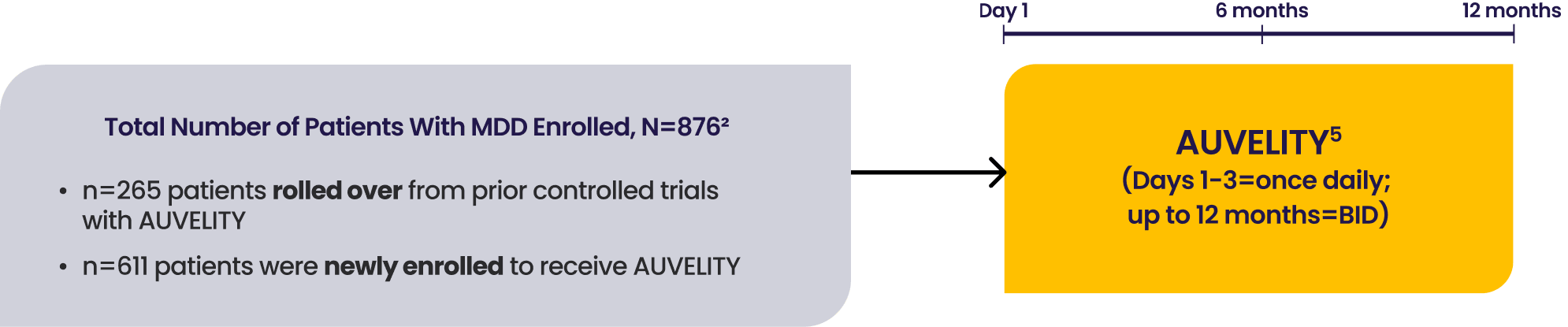
Secondary endpoint results were based on the newly enrolled patients (n=609) and the safety results from the full population (n=876).2,3
All newly enrolled patients were assessed for efficacy through Week 6. Only patients whose MADRS scores improved by ≥25% were eligible to continue in the study. 6% of subjects met discontinuation criteria at Week 6.1,7
Select secondary endpoints include: clinical remission (MADRS total score ≤10), clinical response (≥50% improvement in MADRS total score from baseline), CGI-I, and SDS.1
Clinical response and clinical remission were assessed on the MADRS scale. The MADRS is a clinician-rated scale used to assess depressive symptom severity. Patients are rated on 10 items to assess feelings of sadness, inner tension, reduced sleep or appetite, difficulty concentrating, lassitude, lack of interest, pessimism, and suicidality. Scores range from 0 to 60, with higher scores indicating more severe depression.1,5
BID=twice a day; CGI-I=Clinical Global Impression-Improvement; MADRS=Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale; MDD=major depressive disorder; SDS=Sheehan Disability Scale.